Audio Source
The Audio Source plays back an Audio Clip in the scene. The clip can be played to an Audio Listener or through an Audio Mixer. It can play any type of Audio Clip and can be configured to play as 2D or 3D, or as a mixture.
The audio can be spread out between speakers (stereo to 7.1) (Spread) and morphed between 3D and 2D (Spatialblend).
If the listener is within one or multiple Reverb Zones, reverberation is applied to the source.
There is no limit of how many Audio Sources can have a single object.
Only one Audio Listener is allowed per Scene.
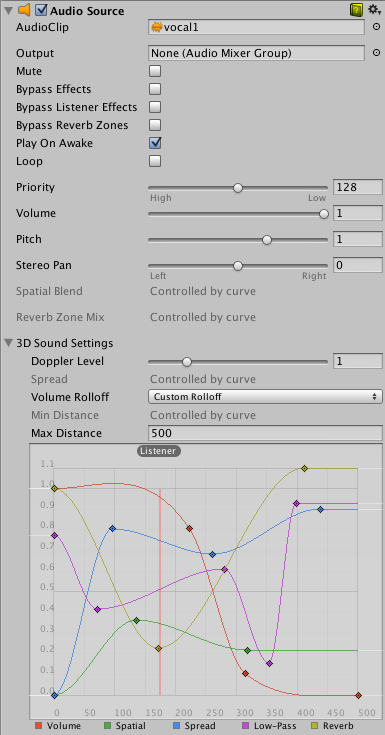
Audio Clip, reference to the sound clip
Output, the sound can be output through an audio listener or audio mixer
Mute, if enabled the sound will be playing but muted
Bypass Effects, quickly turn all effects on/off
Bypass Listener Effects, quickly turn all Listener effects on/off
Bypass Reverb Zones, quickly turn all Reverb Zones on/off
Play on Awake, if enabled, the sound will start playing the moment the scene launches. If not, you need to start it with the Play() command
Loop, enable to make the audio clip loop when it finish
Priority, determines the priority of this audio source among all coexisting in the scene. 0 = most important, 256 = least important, 128 = default. Use 0 to avoid it getting occasionally swapped out
Volume, how loud the sound is at a distance of one world unit from the Audio Listener
Pitch, amount of change in pitch due to slowdown/speed up the audio clip, the default speed is 1
Stereo Pan, sets the position in the stereo field of 2D sounds
Spatial Blend, sets how much the 3D engine has an effect on the audio source
Reverb Zone Mix, sets the amount of the output signal that gets routed to the reverb zones. The amount is linear in the 0 - 1 range, but allows for a 10 dB amplification in the 1 - 1.1 range which can be useful to achieve the effect of near field and distant sounds
3D Sound Settings, settings that are applied proportionally to the spatial blend, here you can modify the outcome of different effects of the sound by the distance between the Audio Listener and the Audio Source, by double click you can add keys to the lines
The values of the curves are Spatial, Volume, Spread, Reverb
Doppler Level, determines how much doppler effect will be applied to this audio source, 0 is no effect
Spread, sets the spread angle to 3D stereo or multichannel sound in speaker space
0 degrees is in the direction of sound, 90 at right angles to each other, 180 opposite each other, 360 opposite to the direction of the sound
Min Distance, the sound will stay at loudest possible within the Min Distance. Outside, it will attenuate
Max Distance, The distance where the sound stops attenuating at
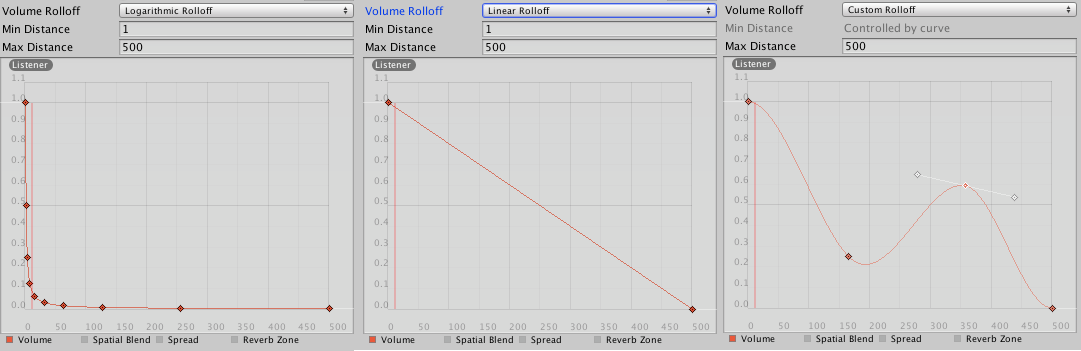
Rolloff Mode, how fast the sound fades. The higher the value, the closer the listener has to be before hearing the sound
Logarithmic Rolloff, the sound is loud when you are close to the source, but it decreases fast at get away, it is the default
Linear Rolloff, the further away from the audio source, the less you can hear it
Custom Rolloff, The sound from the audio source behaves accordingly to how set the graph of roll offs
Doppler Effect

When wave energy like sound or radio waves travels from two objects, the wavelength can seem to be changed if one or both of them are moving. This is called Doppler effect.
It causes the received frequency of a source to differ from the sent frequency if there is motion that is increasing or decreasing the distance between the source and the receiver.
This effect is observable as variation in the pitch of sound between a moving source and a stationary observer.
Doppler Effect does not work in kinematic rigidbodies due they don't have velocity.